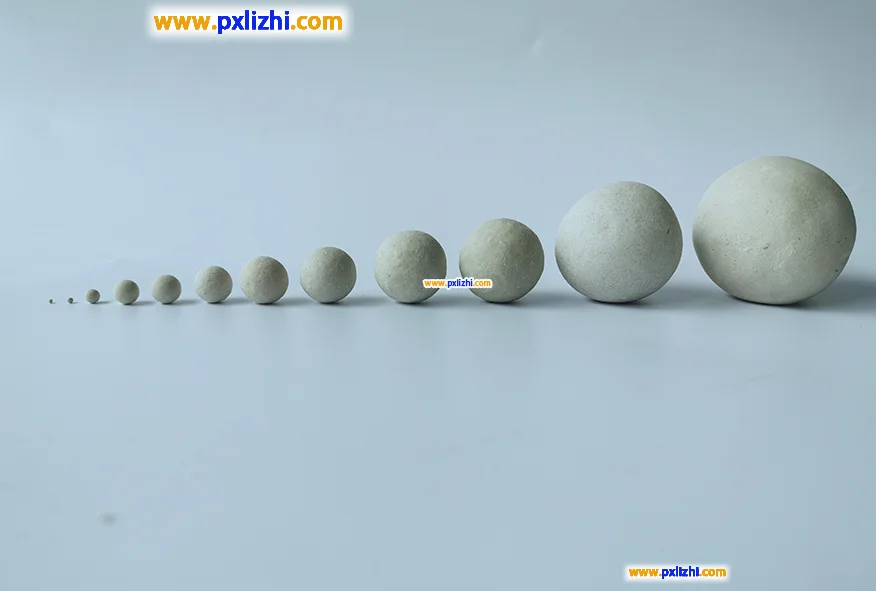

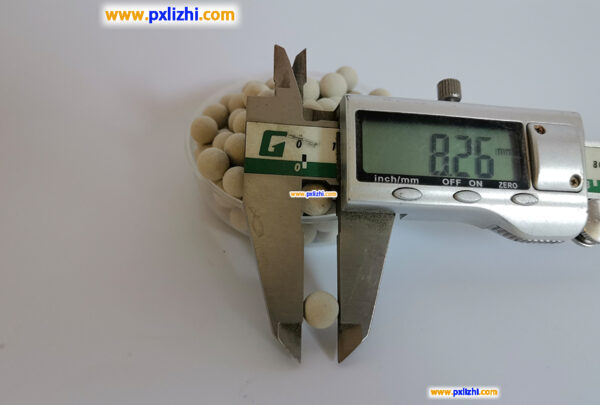
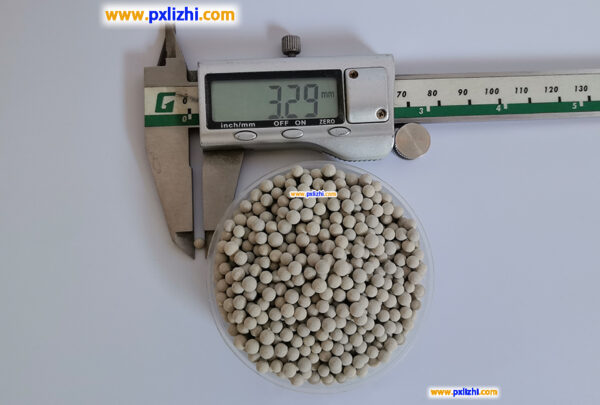
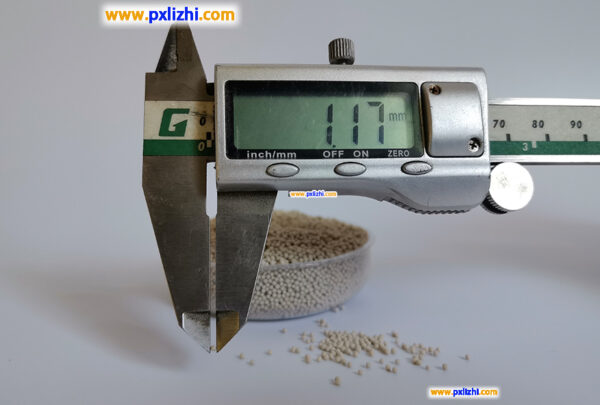
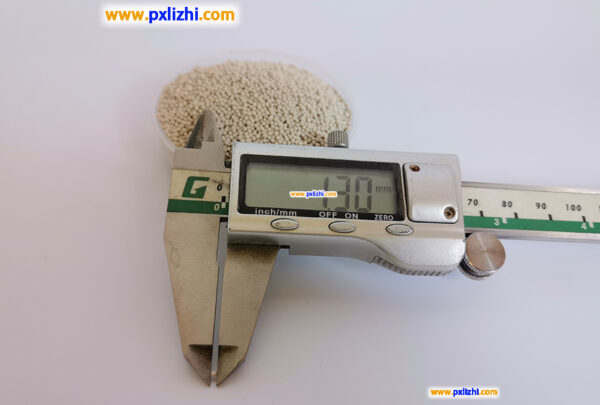
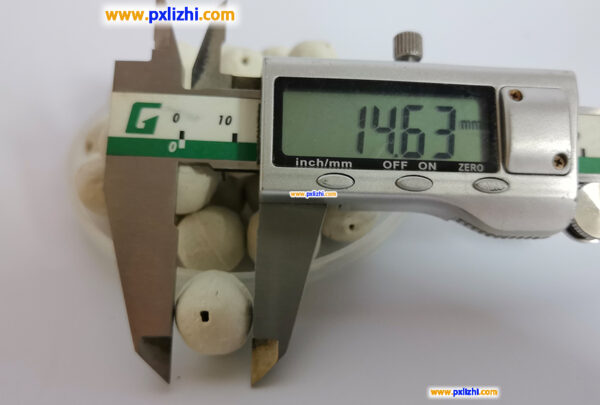
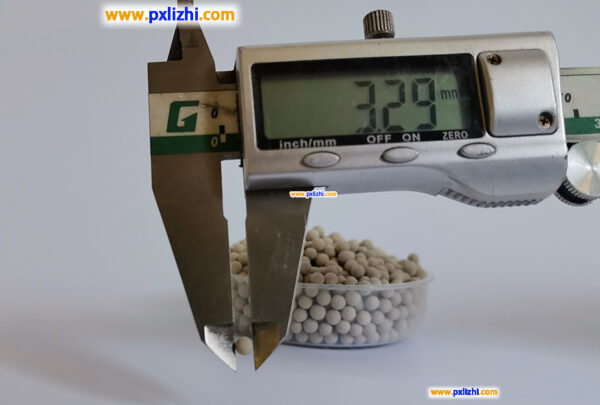
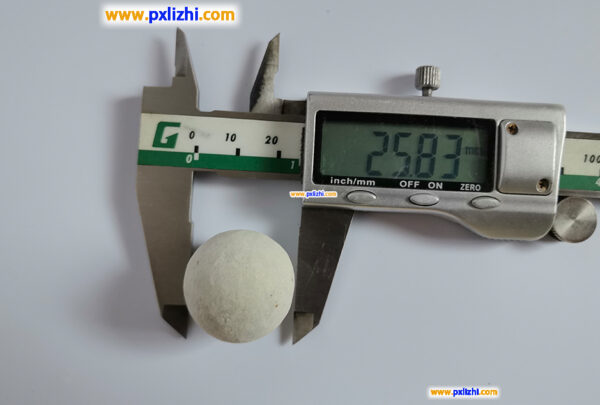
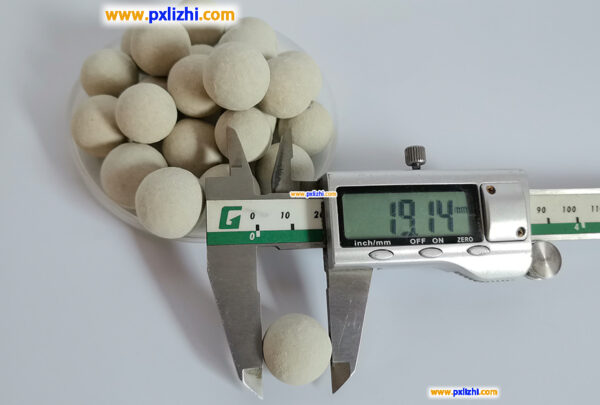
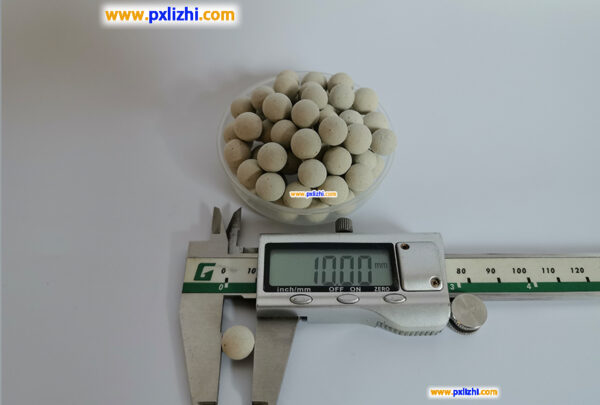
The size specifications of common inert ceramic balls are :3mm, 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, 13mm, 15mm, 19mm, 20mm, 25mm, 30mm, 38mm, 50mm, etc.
Common open hole inert ceramic ball size: Φ10mm, Φ13mm, Φ150mm, Φ20mm, Φ25mm, Φ50mm
Other custom inert ceramic ball specifications: Φ0.8mm-1.5mm, Φ1mm-2mm, etc., because it is a factory, so other specifications and sizes can be directly customized production.
Selection of size
The choice of inert ceramic ball size is usually determined according to the specific use scenario and needs. For example, in fixed-bed reactors, the 2X rule is generally followed, that is, the diameter of the porcelain ball should be twice the diameter of its adjacent catalyst, which results in a more uniform flow or material distribution, a smaller pressure drop, and better reactor operation.








Relation between size and compressive strength
| Diameter (mm) | Diameter range (mm) | Crushing strength (kg/particle) |
Bulk density (kg/m3) |
| 3 (1/8 inch) | 3-5 | 51 | 1800-2000 |
| 6 (1/4 inch) | 6-8 | 102 | 1800-2000 |
| 10 (3/8inch;) | 9-11 | 204 | 1800-2000 |
| 13 (1/2inch) | 12-14 | 306 | 1800-2000 |
| 16 (5/8inch) | 15-17 | 714 | 1800-2000 |
| 19 (3/4inch) | 18-21 | 1020 | 1750-1950 |
| 25 (1inch) | 22-27 | 1429 | 1750-1950 |
| 30 (1 1/4inch) | 28-32 | 1429 | 1750-1950 |
| 38 (1 1/2inch) | 33-38 | 1429 | 1750-1950 |
| 50 (2inch) | 50-55 | 1837 | 1750~1950 |
Inert ceramic ball size has large and small reasons
Adaptable to different catalyst sizes: In practical applications, inert ceramic balls are often used as supporting and covering materials for catalysts in reactors. In order to ensure that the catalyst does not pass through the ceramic ball layer even if the ceramic ball is half broken, the 2X rule is generally followed, that is, the diameter of the ceramic ball should be twice the diameter of the catalyst adjacent to it, so that the material distribution is uniform, the pressure drop is small, and the reactor operation is more optimized. Because the size of the catalyst is different, it is necessary to have different sizes of inert ceramic balls to adapt to it.
Meet different process requirements: Different process has specific requirements for the distribution uniformity and flow rate of materials or air flow. For example, in some processes that need to strengthen the mass transfer process, it may be necessary to use a smaller size of inert ceramic ball to increase the contact area between the material and the porcelain ball, so that the mass transfer is more adequate; In some processes with high pressure drop requirements, a larger size inert ceramic ball may be selected to reduce the resistance of airflow or material passing through.
Adapt to different reactor types and sizes: Different types of reactors, such as fixed bed reactors, fluidized bed reactors, etc., have different requirements for the size and filling method of inert ceramic balls. Large reactors usually require larger sized inert ceramic balls to provide adequate support and stability, while smaller reactors can use smaller sized porcelain balls. In addition, the internal structure and design of the reactor will also affect the size choice of inert ceramic balls, for example, reactors with special shapes or internals may require porcelain balls of a specific size to achieve good filling and fluid distribution.

























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.