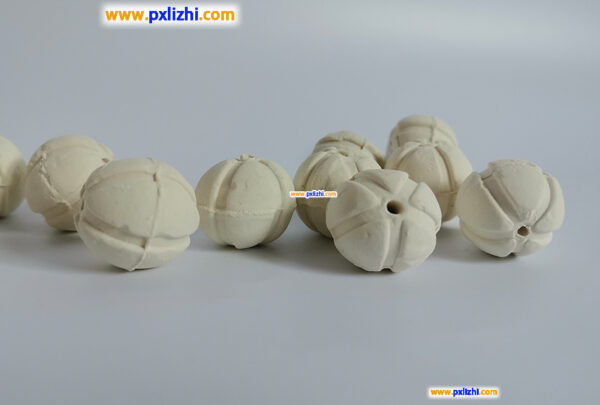
What is refractory ceramic ball?
Refractory ceramic ball is a kind of ceramic sphere made mainly of refractory materials (such as alumina, magnesia, silicoaluminate, etc.) through high-temperature sintering. It has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, high strength, corrosion resistance, and good chemical stability (for some types), and is a commonly used functional filling material in industry. Here, the main focus is on the inert alumina ceramic balls among refractory ceramic balls.

What is its function?
Support and protection: It supports catalysts or other fillers, preventing them from being damaged under pressure, while also dispersing fluids (gases / liquids) to ensure uniform contact with the reaction materials.
High-temperature resistance and heat insulation: It withstands high-temperature erosion in high-temperature environments, reduces heat loss from equipment, and stabilizes the temperature field.
Filtering and purification: It serves as a filtering medium to intercept impurities or enhance gas-liquid contact, thereby improving purification efficiency.
Inert filling: It does not participate in chemical reactions, but only regulates the reaction space, flow rate, or prevents local overheating.
Technical Datas:
| Item | Value |
| (%)Water absorption (%) | <0.5 |
| (g/cm3) Bulk density (g/cm3) | 1.35-1.4 |
| (g/cm3) Specific gravity (g/cm3) | 2.3-2.4 |
| (%)Free volume (%) | 40% |
| (℃)Operation temp.(max) (℃) | 1200 |
| (scale)Moh’s hardness (scale) | >6.5 |
| (%) Acid resistance (%) | >99.6 |
| (%)Alkali resistance (%) | >86 |
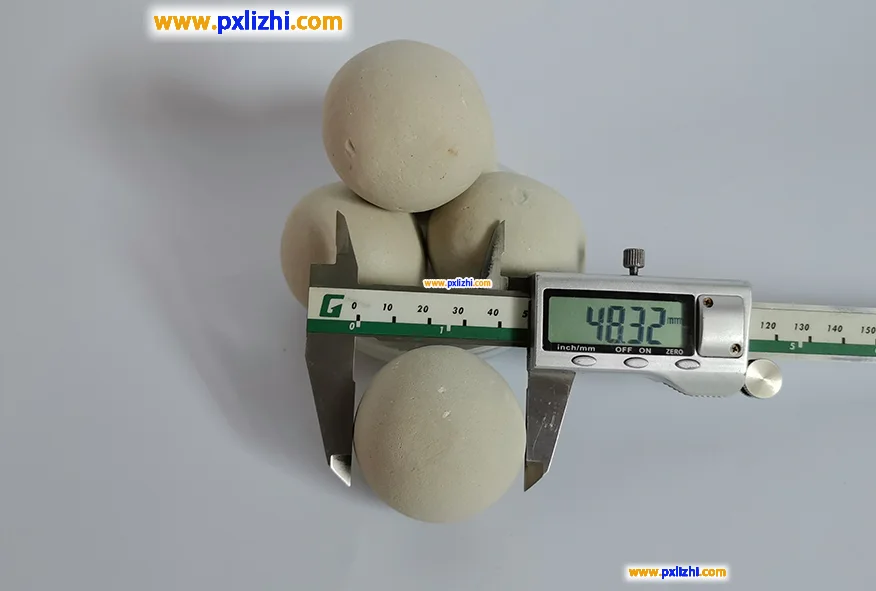

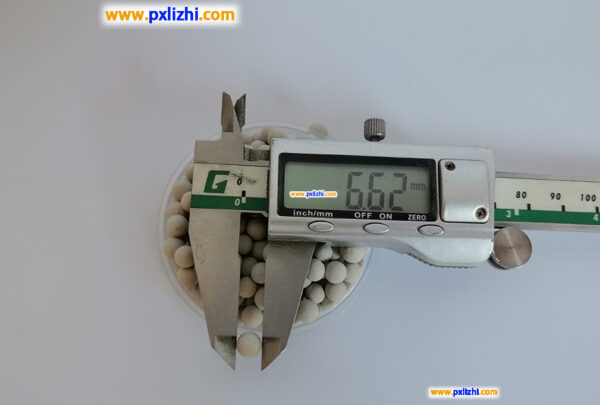
Crush Strength:
| Size | Crush strength | |
| Kg/particle | KN/particle | |
| 1/8″ (3mm) | >35 | >0.35 |
| 1/4″ (6mm) | >60 | >0.60 |
| 3/8″ (10mm) | >85 | >0.85 |
| 1/2″(13mm) | >185 | >1.85 |
| 3/4″ (19mm) | >487 | >4.87 |
| 1″ (25mm) | >850 | >8.5 |
| 1-1/2″ (38mm) | >1200 | >12 |
| 2″ (50mm) | >5600 | >56 |
Where is it used?
Petrochemical / Coal Chemical Industry: As a catalyst support layer in reaction towers (hydrogenation, catalytic cracking, etc.).
High-temperature Furnaces: As a filling or insulation material in ceramic kilns, metallurgical furnaces, etc., to reduce heat loss.
Environmental Protection / Water Treatment: Used in purification towers and filtration equipment to filter impurities or adsorb pollutants.
Fertilizer / Pharmaceutical Industry: As an inert filler in reactors to optimize reaction conditions.
Factors Affecting the Service Life of Refractory Ceramic Balls
Temperature and Thermal Shock: The higher the temperature and the more drastic the temperature changes, the shorter the service life of refractory ceramic balls.
Chemical Corrosion: Alkali, acid, molten slag, and strong oxidizing atmosphere can accelerate erosion.
Mechanical Abrasion: High-speed gas or liquid flow and particle impact cause wear.
Installation and Maintenance: Uneven loading, bypass flow, and bed collapse can significantly shorten the service life of refractory ceramic balls.
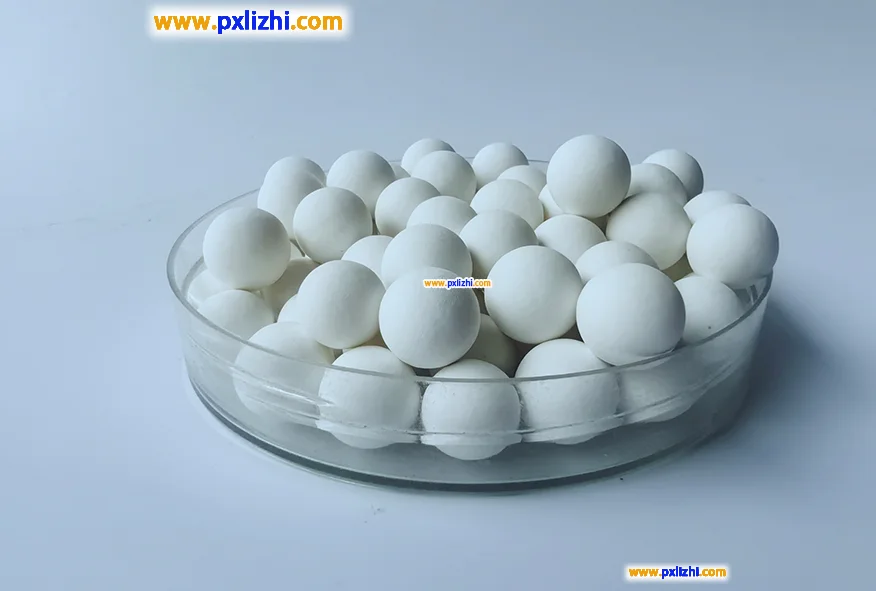

The differences between refractory ceramic balls and inert alumina ceramic balls
Refractory ceramic balls are a broader category, referring to ceramic spheres with refractory properties such as high temperature resistance and high strength. Their materials can be various refractory materials such as alumina, magnesia, zirconia, and silicate alumina. Inert alumina ceramic balls are a type of refractory ceramic balls, with the main component being alumina (Al₂O₃). They are called “inert” because of their stable chemical properties and non-reaction with the treated medium.
The “inertness” of inert alumina ceramic balls is their key characteristic, making them suitable for scenarios where chemical reactions need to be avoided (such as catalyst support, filtration, filling, etc.); while other refractory ceramic balls may not necessarily be “inert” due to different materials (for example, some refractory ceramic balls containing active components may participate in specific reactions).
In conclusion: Inert alumina ceramic balls fall within the category of refractory ceramic balls, but not all refractory ceramic balls are inert alumina ceramic balls; they also include refractory spheres made of other materials.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.