What are high-temperature inert ceramic balls?
High-temperature inert ceramic balls are a type of industrial ceramic product in the form of spherical shapes, which are mainly composed of ceramic materials such as alumina and are obtained through high-temperature sintering. They possess strong chemical stability, excellent high-temperature resistance (typically able to withstand temperatures of several thousand degrees Celsius), high physical and mechanical strength, and do not undergo chemical reactions with the contacting medium. They are widely used in reactors and towers in fields such as petrochemicals, metallurgy, and environmental protection, serving functions such as supporting catalysts, distributing gas or liquid flow, and filtering impurities. They are called “inert” because they can maintain stable physical and chemical properties under harsh conditions.
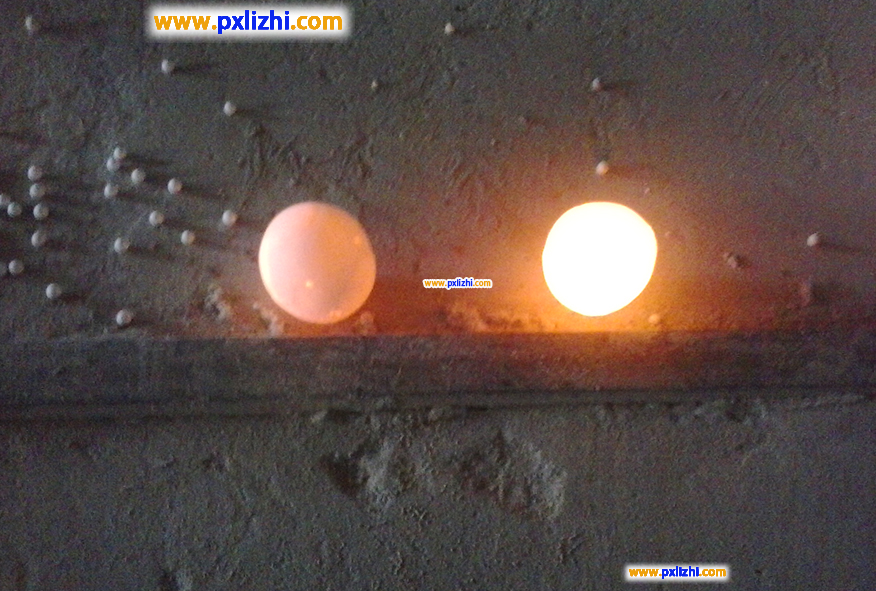
What are the temperature resistances of ordinary inert ceramic balls and high-aluminum inert ceramic balls?
Ordinary inert ceramic balls are usually made from main raw materials such as clay and feldspar, and their temperature resistance is relatively low, generally ranging from 900℃ to 1100℃; while high-aluminum inert ceramic balls have a higher content of alumina (usually above 80%, and in some cases up to over 99%), and thus have better high-temperature resistance. Their temperature resistance is usually between 1200℃ and 1700℃, and specific values will increase as the content of alumina increases.
Why are strength-inert ceramic balls resistant to high temperatures?
High-temperature inert ceramic balls need to have high-temperature resistance because they are mainly used in high-temperature working environments such as petrochemical catalytic reactions, metallurgical smelting, and high-temperature gas filtration. The temperatures in these scenarios often reach hundreds or even thousands of degrees Celsius. Without high-temperature resistance, the ceramic balls would be damaged by high temperatures, resulting in a decrease in strength, even melting, decomposition, or chemical reactions with surrounding media (such as high-temperature reactants or corrosive gases), thereby losing their core functions of supporting catalysts and evenly distributing fluids, and unable to ensure the stable operation of industrial equipment and process efficiency.
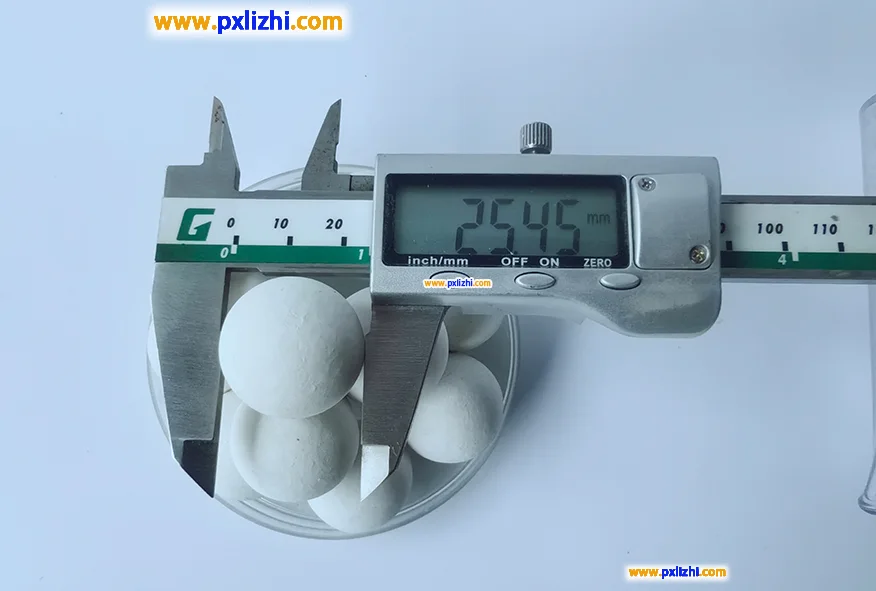

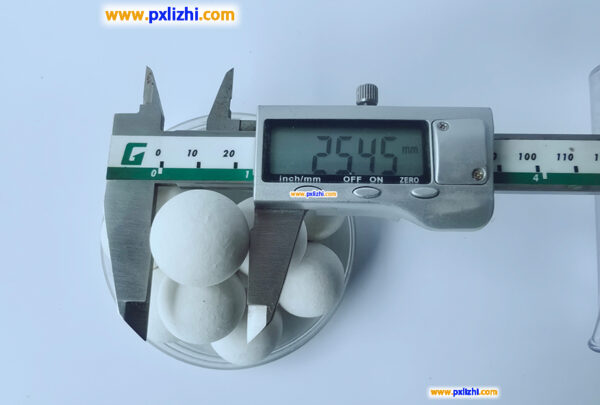
Which devices require the use of high-temperature-resistant inert ceramic balls?
High-temperature-resistant inert ceramic balls are widely used in hydrogenation reactors, catalytic cracking units, desulfurization towers, absorption towers in the petrochemical industry, gasifiers and synthesis towers in coal chemical industry, high-temperature calciners and smelting furnaces in the metallurgical industry, high-temperature smoke gas treatment devices and waste incineration equipment in the environmental protection field, as well as ammonia synthesis towers and sulfuric acid conversioners in fertilizer production, all of which need to support catalysts, distribute gas or liquid flow, filter or provide insulation in high-temperature, high-pressure or corrosive environments.
Technical Data
| Item | Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3 | Type 4 |
| Equal to | Denstone 2000 | Denstone 57 | Denstone 99 | |
| AL2O3 | 17-19% | 23-26% | 90% | >99% |
| Acid resistance | >=98% | |||
| Alkali resistance | >80% | >82% | >90% | >95% |
| Thermal shock reistance | >=300 | >=400 | >=700 | >=800 |
| Operation temperature (℃) | 982 | 1100 | 1350 | 1500-1600 |












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.