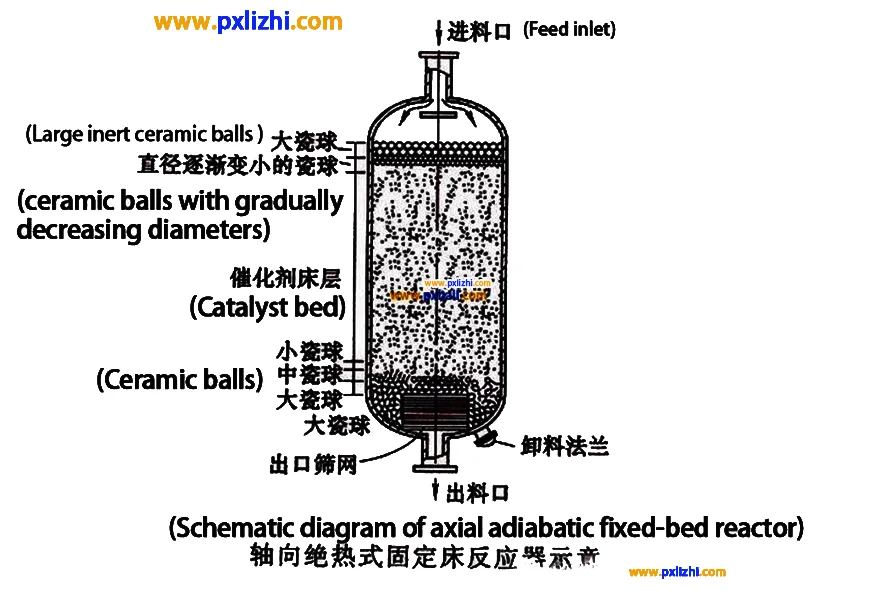
Inert ceramic ball action in reactor
Supporting catalyst: Inert ceramic balls are usually placed on the bottom and top of the catalyst bed inside the reactor. When at the bottom, it can carry the weight of the catalyst above, so that the catalyst is evenly distributed, avoiding the catalyst directly in contact with the reactor wall and causing local pressure or catalyst leakage. The inert ceramic ball placed on the top can prevent the loosening and displacement of the catalyst bed due to air flow impact and other reasons during the operation of the device, and play a role in stabilizing the bed.
Uniform distribution of air or liquid flow: When the reaction material enters the reactor, the inert ceramic ball can play the role of dispersion and uniform distribution of air or liquid flow. Through its irregular stacking structure, the material can pass through the catalyst bed more evenly, avoiding the phenomenon of bias flow and ditch flow, so as to improve the contact efficiency between the material and the catalyst in the reactor, make the reaction more adequate and stable, and help to improve the conversion rate and selectivity of the reaction.
Protection of the catalyst: On the one hand, the inert ceramic ball can block the solid impurities that may exist in the reactor, prevent them from entering the catalyst bed, prevent impurities from blocking the catalyst pore or covering the catalyst active site, thereby extending the service life of the catalyst. On the other hand, in some reaction processes, local overheating may occur, the inert ceramic ball has a certain heat storage and thermal conductivity, which can alleviate the damage of local overheating to the catalyst to a certain extent, and play a role in protecting the catalyst.

Application device
Petrochemical industry: In the catalytic cracking unit, as the supporting material of the catalyst, the catalyst bed is carried to ensure the uniform passage of oil and gas through the catalyst, so that the large molecular hydrocarbons in the crude oil are efficiently cracked into small molecular products. In the hydrofining unit, it is used to support and protect the catalyst, so that the reaction material is evenly distributed, and the efficiency and selectivity of the hydrogenation reaction are improved.
Fertilizer industry: Used in synthetic ammonia conversion furnace, support and protect the catalyst, while making the gas evenly distributed, promote the conversion reaction of carbon monoxide and water vapor, and improve the production and quality of synthetic ammonia. In addition, inert ceramic balls can also be seen in high and low temperature conversion furnaces, hydroconverters, desulfurization tanks and methane conversion furnaces in chemical fertilizer plants, which play the role of supporting and protecting catalysts and evenly distributing gases or liquids.
Natural gas industry: In the natural gas purification device, the protection of desulfurization, decarbonization and other catalysts to avoid the impact of air flow caused by catalyst powder, to ensure that the impurities in the natural gas are effectively removed, improve the purity of the gas.

The use of inert ceramic balls in the reactor:
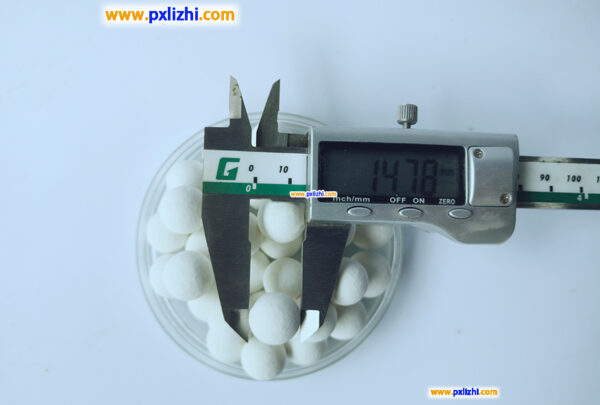
Size: According to the size of the reactor, catalyst particle size and material flow characteristics and other factors, select the appropriate size of the inert ceramic ball.
Quality: Ensure that the inert ceramic ball has sufficient strength to withstand the weight of the catalyst and material and the pressure change during the reaction process, while ensuring its chemical stability and thermal stability is good, to avoid biochemical reaction or crushing under reaction conditions.
Uniformity: When loading inert ceramic balls, it is necessary to ensure that they are evenly distributed in the reactor, otherwise it may lead to material drift and affect the reaction effect.
Height and position: The loading height and position of the inert ceramic ball are controlled strictly according to the design requirements.
Before loading: Inert ceramic balls may be contaminated with dust, oil and other impurities during storage and transportation, and should be cleaned and dried before loading to prevent these impurities from entering the reactor and causing pollution to the catalyst and reaction materials.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.