Introduction
Inert ceramic balls for catalyst support are ceramic spherical materials with stable chemical properties that do not participate in catalytic reactions. Their primary function is to support and protect catalysts, improve catalyst dispersion, and optimize fluid distribution inside reactors. By creating a stable and uniform reaction environment, inert ceramic balls help ensure efficient and long-term catalytic performance.

Key Characteristics and Functions
Chemical Inertness as the Core Feature
Inert ceramic balls are characterized by excellent chemical stability. They are resistant to high temperatures, acids, and alkalis, and do not react with reactants or catalysts. This inert behavior prevents contamination or interference with catalytic reactions, ensuring consistent and reliable process results.
Auxiliary but Critical Functions
Although they do not act as catalysts themselves, inert ceramic balls play an essential supporting role:
-
Catalyst Support Structure: They provide a stable framework for catalysts, allowing catalysts to be evenly distributed or partially deposited on their surface or within pores, improving catalyst utilization efficiency.
-
Protection and Flow Distribution: Installed above and below catalyst beds, inert ceramic balls support the catalyst layer, prevent catalyst breakage caused by high-speed fluid impact, and promote uniform gas or liquid distribution throughout the reactor.
Main Application Areas
Petrochemical Industry
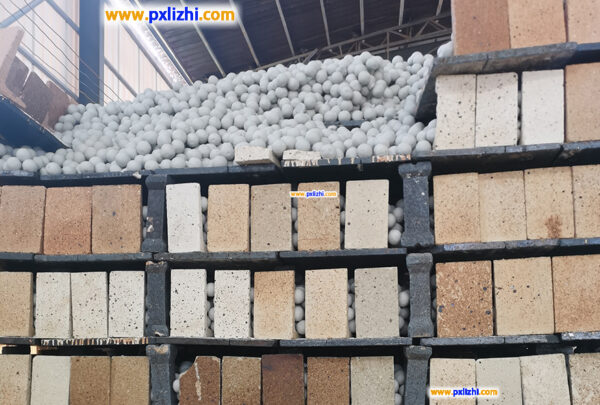
This is the largest application field for inert ceramic balls. In refining units such as hydrocracking, catalytic reforming, hydrotreating, desulfurization, and denitrification systems, inert ceramic balls are placed at the top and bottom of catalyst beds. They protect catalysts from erosion, pulverization, and channeling while ensuring uniform flow of oil or gas through the reaction zone.
Coal Chemical Industry
In processes such as coal gasification, coal liquefaction, ammonia synthesis, and methanol synthesis, inert ceramic balls are widely used due to their ability to withstand high temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive gases. They help protect catalysts and improve the stability and efficiency of synthesis reactions.
Fine Chemical Industry
Inert ceramic balls are used in reactors for esterification, hydrogenation, oxidation, and other fine chemical processes. They are especially suitable for applications with mild reaction conditions and catalysts that are sensitive or prone to mechanical damage.
Environmental Protection Industry
In environmental applications, inert ceramic balls are used in catalytic systems for industrial waste gas and wastewater treatment, such as SCR/SNCR flue gas denitrification systems and catalytic oxidation reactors for organic wastewater. Their inertness and durability ensure long-term and stable operation of environmental treatment equipment.

Service Life of Inert Ceramic Balls for Catalyst Support
The service life of inert ceramic balls mainly depends on operating conditions, material quality, and operation and maintenance practices. Under normal conditions, the typical service life ranges from 2 to 5 years. In extreme operating environments, it may be reduced to less than 1 year, while high-quality materials combined with proper operation can extend service life to more than 5 years.
Key Factors Affecting Service Life
-
Corrosive Media and Temperature: Strong acids, strong alkalis, and highly oxidative media can gradually damage the ceramic surface and internal pores. Frequent thermal shocks caused by rapid heating and cooling may lead to cracking. More severe corrosion and temperature fluctuations result in shorter service life.
-
Fluid Erosion and Abrasion: High fluid velocities and the presence of solid impurities can continuously erode the ceramic ball surface, leading to wear, pulverization, or breakage. In high-flow units such as hydroprocessing reactors, service life is typically around 2–3 years.
-
Material Strength and Composition: High-alumina ceramic balls with higher Al₂O₃ content offer superior mechanical strength and corrosion resistance compared to ordinary ceramic balls. Their service life can be 1–2 times longer under the same operating conditions.
-
Operation and Maintenance: Frequent start-ups and shutdowns, as well as large pressure fluctuations, accelerate mechanical damage. Stable operation and regular removal of impurities can significantly extend the service life of inert ceramic balls.

Inert Alumina Ceramic Ball for Catalyst Support













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.