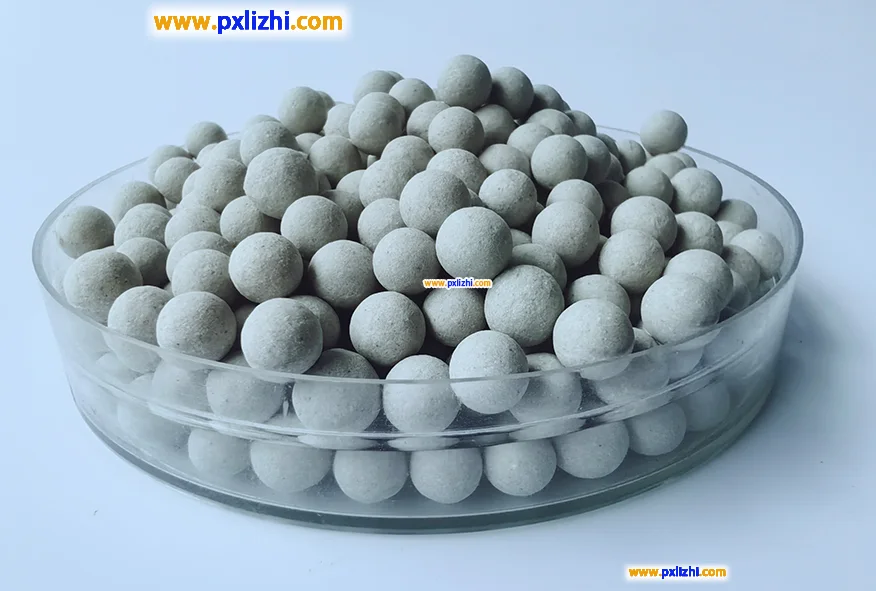
The definition of catalyst ceramic balls
Catalyst ceramic balls are spherical particles made of high-temperature and corrosion-resistant ceramic materials (such as alumina, silica, etc.), featuring high strength, high chemical stability and specific physical structures (such as porosity, specific surface area, etc.). Its preparation process usually includes raw material proportioning, molding, sintering and other techniques. Depending on different application scenarios, the size and performance parameters will be adjusted.
The main function of the catalyst ceramic balls
Support and protect the catalyst
In chemical reactors, catalyst ceramic balls are usually laid at the bottom or top of the catalyst bed as a support layer. It can evenly distribute the fluid (gas or liquid), preventing the catalyst particles from directly contacting the reactor wall or being impacted by the fluid, thereby reducing the wear, breakage and clogging of the catalyst and extending its service life.
For example, in the hydrogenation reactor of petroleum refining, porcelain balls can prevent the catalyst from being lost due to the scouring of high-pressure fluid.
2. Evenly distribute the fluid and heat
The porous structure and regular spherical shape of the ceramic balls endow them with excellent fluid distribution capabilities, ensuring that the reaction media (such as feedstock gas and liquid-phase reactants) pass uniformly through the catalyst bed, thus avoiding uneven reactions caused by overly rapid or slow local flow rates.
Meanwhile, the porcelain balls can assist in conducting heat during the reaction process, preventing local overheating or uneven temperature in the catalyst bed, and maintaining the stability of the reaction temperature (which is particularly crucial in exothermic or endothermic reactions).
3. Pre-treat reactants or adsorb impurities
Some ceramic balls have undergone special treatment (such as loading active components or having adsorption functions), which can remove impurities (such as water, sulfides, heavy metals, etc.) from the reactants before the reaction, reducing the risk of catalyst poisoning.
For instance, in natural gas conversion reactions, porcelain balls can first adsorb dust or acidic substances in the gas, protecting the activity of subsequent catalysts.
The application fields of catalyst ceramic balls
1. Petrochemical and oil refining industry
Hydrogenation reaction: It is used in hydrogenation refining and hydrogenation cracking reactors to support the catalyst and filter mechanical impurities in the feedstock.
Catalytic reforming: Evenly distribute oil and gas in the reforming reactor to assist in heat transfer.
Catalytic cracking: As the bottom support of the fluidized bed reactor, it prevents the leakage of catalyst particles.
2. Coal chemical industry and Syngas preparation
Coal gasification: Supporting the catalyst in the gasifier while pre-treating impurities in the syngas.
Methanol synthesis: Laid at the bottom of the synthesis tower, the synthesis gas (CO, H₂) is evenly distributed to ensure sufficient contact of the catalyst.
3. Environmental protection and energy fields
Waste gas treatment: In the catalytic combustion device for VOCs (volatile organic compounds), support the catalyst and evenly distribute the waste gas to enhance the purification efficiency.
Hydrogen energy: In the hydrogen purification device of fuel cells, impurities are adsorbed by ceramic balls to protect the electrode catalyst.
 Best low alumina ball
Best low alumina ballSummary
Although catalyst ceramic balls are not core catalysts, they ensure the efficiency and lifespan of the catalyst through functions such as support, gas distribution, and heat transfer in chemical reactions. They are indispensable auxiliary materials in reactor design. Its application covers multiple fields such as energy, environmental protection, and chemical engineering. By choosing the appropriate materials and specifications based on specific working conditions, the stability and economy of the process can be significantly enhanced.
 Wholesale inert ceramic ball
Wholesale inert ceramic ball