Preface
I can offer you a discounted price for the catalyst support balls because we are a professional manufacturer of catalyst support balls with many years of experience, so the quality is guaranteed. At the same time, we have various specifications and types of regular catalyst support balls in stock to meet the needs of emergency delivery.
Price
Wholesale price of low-alumina catalyst support balls: around 420 US dollars
The wholesale price of medium aluminum catalyst support balls is around 700 US dollars
Wholesale price of high alumina catalyst support balls: around 1,400 US dollars
Note: The above prices are approximate. For an accurate quotation, please provide the purchase quantity of the catalyst support balls, packaging requirements, technical parameter requirements, transportation destination, etc.

Contact information
Email: lizhi@pxball.Cn
Wechat ID: pxlizhi
Company website: www.Pxlizhi.Com
What factors affect the service life of catalyst support balls?
The physical effects of the reaction environment: High temperatures may cause sintering, softening or uneven thermal expansion of the material, leading to cracking. High pressure or pressure fluctuations will intensify the squeezing and collision between the spherical particles, causing mechanical damage. Continuous scouring by fluids, especially those with high flow rates or containing solid particles, can lead to surface wear, reduced particle size, and even breakage.
Chemical corrosion and erosion: Acids, bases, salts or strong oxidants in the reaction system can undergo chemical reactions with the material of the support balls (such as the dissolution of alumina in strong acids and the pulverization of quartz in strong bases), leading to material deterioration and a decrease in strength. If there are organic solvents or high-temperature molten substances present, the spheroidal structure may be damaged through penetration or swelling.
Mechanical stress and loading issues: The long-term heavy pressure caused by the sedimentation of the catalyst layer and the sudden temperature changes during the start-up and shutdown of the reactor (thermal shock) can lead to stress concentration inside the spherules, causing cracks. If the particle size gradient is unreasonable, impurities are present or the local accumulation is too dense during filling, it will accelerate local wear or uneven force distribution, and speed up damage.
The inherent performance limitations of the material: If the compressive strength, wear resistance, high-temperature resistance or corrosion resistance of the material do not match the actual working conditions (such as ordinary ceramics used in ultra-high-temperature environments), it will fail prematurely due to the insufficiency of the material’s own performance.
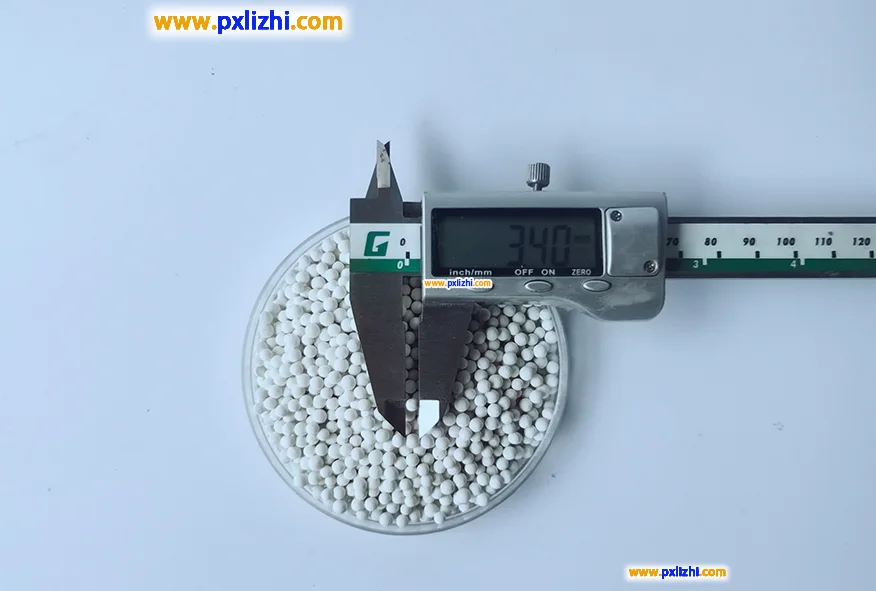

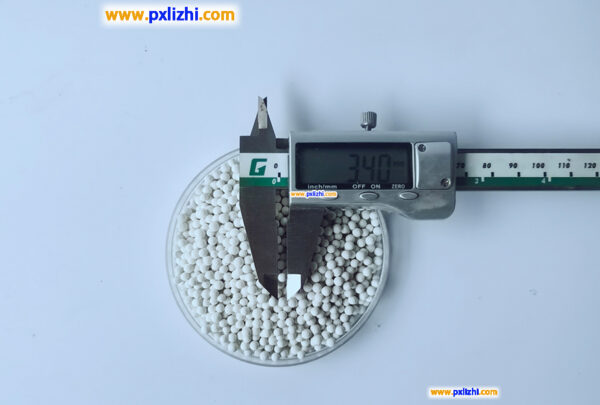
What problems should be avoided when loading catalyst support balls?
Avoid confusion in particle size matching: If the filling is not carried out in a gradient of “large particle size at the bottom and small particle size at the top”, it is easy to cause uneven fluid distribution and excessive pressure drop.
Avoid filling that is too loose or too dense: If it is too loose, it can easily cause the spherical particles to shift and the catalyst layer to shake; if it is too dense, it will increase fluid resistance and affect the mass transfer efficiency.
Avoid mixing in impurities or damaged balls: Impurities may contaminate the catalyst or clog the channels, and damaged balls will reduce the support strength and accelerate overall wear.
Avoid uneven local accumulation: For instance, if one side is too high and the other side is too low, it will cause fluid diversion and reduce the utilization rate of the catalyst.
Avoid not cleaning the inner walls of the reactor: Residual rust, dust, etc. will adhere to the surface of the support balls, affecting their stability and fluid flow.













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.