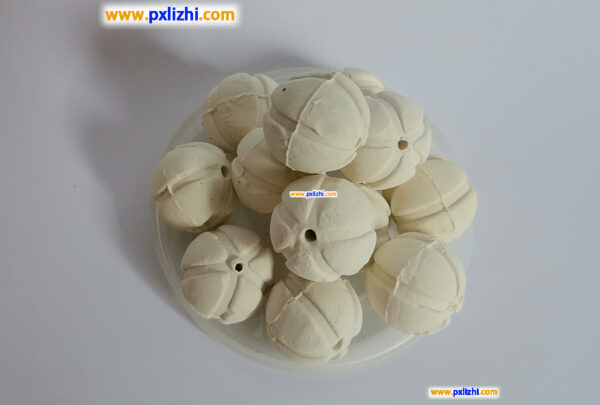
Definition
Catalyst support media ceramic balls are inert or active ceramic fillers made with alumina, silica, or other composite oxides as the main raw materials, through high-temperature sintering. They possess characteristics such as high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and stable chemical properties. Primarily applied in catalytic reaction devices within industries including petrochemicals, chemical fertilizers, fine chemicals, and environmental protection, they serve the functions of supporting, protecting, dispersing, and carrying catalysts.

Functions
Functions of Catalyst Support Media Ceramic Balls
- Support and Dispersion Function: In reaction towers or reactors, ceramic balls can support the catalyst layer, enabling uniform distribution of gas or liquid and preventing catalyst agglomeration or uneven flow.
- Catalyst Protection: Acting as a buffer layer, they prevent catalyst particles from being broken due to the high-speed impact of reactants, thereby extending the service life of catalysts.
- Enhancing Mass Transfer Efficiency: Their porous structure facilitates the diffusion and adsorption of reactants, increasing the reaction rate.
- Stabilizing System Operation: Ceramic balls can withstand significant temperature changes and pressure fluctuations, ensuring the long-term stable operation of reaction devices.
Applications of Catalyst Support Media Ceramic Balls
- Petrochemical Equipment: Used as a support and protection layer in reactors for processes such as hydrogenation, cracking, reforming, desulfurization, and denitrification.
- Chemical Fertilizer Industry: Applied as a catalyst filling layer in ammonia synthesis towers and methanol synthesis towers.
- Environmental Protection Equipment: Utilized as an adsorption and purification medium in waste gas and wastewater treatment towers.
- Pharmaceutical and Fine Chemical Industry: Employed as a reaction carrier in reaction kettles and absorption towers.
- Heat Recovery Systems: Used as heat exchange fillers to improve heat exchange efficiency.

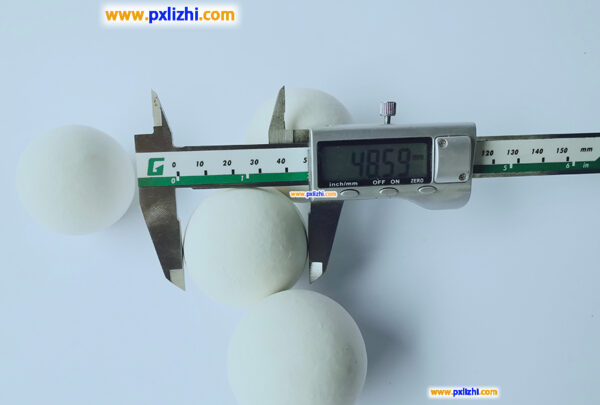
Technical Parameters
Physical Values
| Item | Value |
| Water Absorption | <0.5% |
| Bulk Density (MT/m³) | 1.35-1.4 |
| Specific Gravity | 2.3-2.4 |
| Free Volume | 40% |
| Operation Temp. (max) | 1100℃ |
| Moh’s Hardness | >6.5 scale |
| Acid Resistance | >99.6% |
| Alkali Resistance | >85% |
| Spalling Resistance | 300℃ |
| Size | Crush Strength | Crush Strength |
| Kg/particle | KN/particle | |
| 1/8’’ (3mm) | >35 | >0.35 |
| 1/4’’ (6mm) | >60 | >0.60 |
| 3/8” (10mm) | >85 | >0.85 |
| 1/2’’ (13mm) | >185 | >1.85 |
| 3/4’’ (19mm) | >487 | >4.87 |
| 1’’ (25mm) | >850 | >8.5 |
| 1.5’’ (38mm) | >1200 | >12 |
| 2’’ (50mm) | >5600 | >56 |
Chemical Composition
| Al₂O₃ + SiO₂ | Al₂O₃ | SiO₂ | Fe₂O₃ | MgO | K₂O + Na₂O + CaO | Other |
| > 92% | 17-23% | 73-77% | <1% | <0.5% | <4% | <1% |

Types
- Inert Alumina Ceramic Balls: Mainly used to support and protect the catalyst layer, with no participation in chemical reactions.
- Activated Alumina Balls: Possess strong adsorption performance, and are often used as desiccants and purification adsorption media.
- High-Alumina Ceramic Balls (≥90% Al₂O₃): Feature excellent high-temperature resistance, suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure reaction systems.
- Porous Ceramic Balls: Open-pore ceramic balls have numerous regular or irregular open-pore structures on their surface and inside, which are interconnected to form a complex pore network.
- Porous Catalyst Support Balls: Have a high specific surface area, and are used to load various catalytic active components.
- Micro-Pore Ceramic Balls: The interior of micro-pore ceramic balls contains a large number of tiny pores, with pore sizes usually ranging from nanometers to micrometers, and they have an extremely high specific surface area.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.