What are the chemical components of inert ceramic balls and what roles do they play? Also, why does the aluminum content in inert ceramic balls have a significant impact on the price?
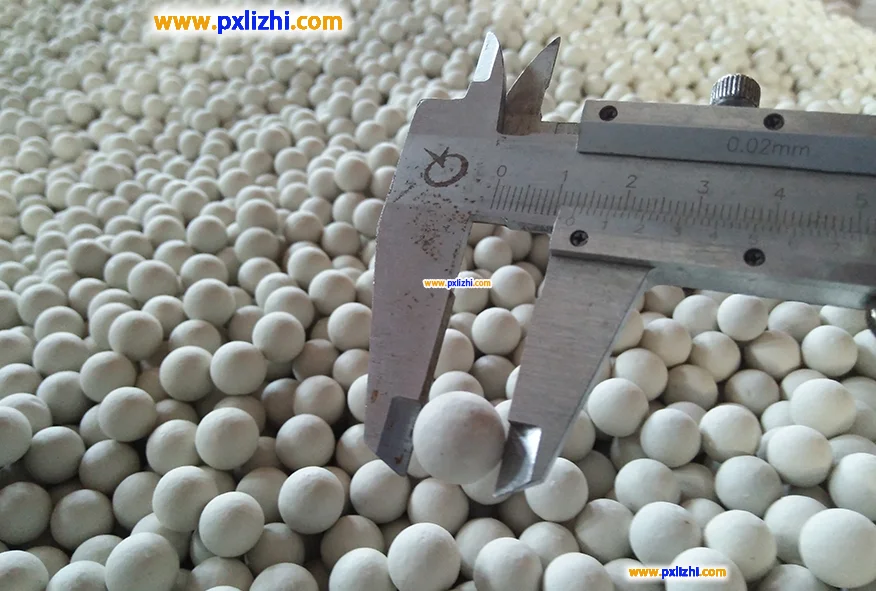

- Main Chemical Components and Functions of Inert Ceramic Balls
The chemical composition of inert ceramic balls mainly consists of inorganic oxides with high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. The core components and their functions are as follows:
Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃): The content is usually between 30% and 95%, which is the core component determining the performance of the ceramic balls. It can provide high strength, high hardness, and excellent high-temperature resistance (able to withstand temperatures above 1200°C), while enhancing the resistance to acidic and alkaline corrosive media, ensuring the stable performance of the ceramic balls in complex conditions.
Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂): The content is approximately 5% to 30%, and its main function is to adjust the density and firing performance of the ceramic. It can reduce the firing temperature, reduce production costs, and improve the thermal shock resistance (avoid cracking due to sudden temperature changes), and enhance wear resistance.
Calcium Oxide (CaO) and Magnesium Oxide (MgO): The total content usually does not exceed 5%, and they exist as fluxes. During firing, they promote the fusion and combination of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, reducing porosity and improving the density and mechanical strength of the ceramic balls.
Iron Oxide (Fe₂O₃): The content is generally less than 1%, mostly as impurities or trace additives. In small amounts, it can act as a coloring agent, but excessive amounts will reduce high-temperature resistance and chemical stability, so it needs to be strictly controlled.
Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) (optional): In some high-aluminum ceramic balls, 1% to 3% is added, used to refine the crystal grains, enhancing strength, impact resistance, and corrosion resistance to specific media.
- The Core Functions of Inert Ceramic Balls
The “inertness” of inert ceramic balls refers to their inability to undergo chemical reactions with the contacting media (such as gases, liquids, catalysts, etc.). Based on this, they mainly play three major roles:
- Supporting Function: Supporting the catalyst or filler to prevent them from breaking or sinking due to gravity or fluid impact, maintaining the stability of the bed structure.
- Distributing Fluids: Through regular stacking, evenly distributing gases or liquids, avoiding “channel flow” and “biased flow” phenomena, improving reaction or filtration efficiency.
- Isolating Layers: Separating different types of catalysts or fillers, preventing contamination and ensuring that each layer can independently perform its function.

III. Reasons for the significant impact of aluminum content on the price of inert ceramic balls
The content of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) is a key factor influencing the price of inert ceramic balls. The main reasons are as follows:
- Differences in raw material costs: The price of high-purity aluminum oxide (such as industrial-grade aluminum oxide powder) is much higher than that of other components like silicon dioxide. The higher the aluminum content (such as high-aluminum balls with Al₂O₃ ≥ 90%), the greater the proportion of raw material costs in the final product price.
- Complexity of production process: High-aluminum ceramic balls require higher firing temperatures (usually above 1600°C) and longer holding times to ensure that the aluminum oxide is fully sintered. This increases energy consumption and production time costs; while low-aluminum balls (with Al₂O₃ ranging from 30% to 50%) have lower firing temperatures and simpler processes, resulting in lower costs.
- Performance premium: High-aluminum balls have superior strength, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance compared to low-aluminum balls. They are suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature, and highly corrosive scenarios (such as petroleum cracking towers, chemical reaction vessels), and the market demand for their performance supports a higher price positioning.
Therefore, the aluminum content is directly related to the cost of raw materials, the difficulty of production, and the performance of the product. This ultimately leads to significant price differences for inert ceramic balls with different aluminum contents.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.